CONTENTS OF THIS REPORT
INTRODUCTION
This research report explores the effects of music on the brain, analyzing its psychological, physiological, and cognitive impacts, with a focus on memory, emotions, attention, and overall cognitive functioning.
The Cognitive Effects of Music
- Memory Enhancement
- Attention and Focus
- Cognitive Processing Speed
Emotional and Psychological Effects of Music
- Mood Regulation
- Therapeutic Applications
- Stress Reduction
CONCLUSION
AIMS OF THIS REPORT
This research report aims to explore the extensive effects of music on the brain, providing a comprehensive analysis of its psychological, physiological, and cognitive impacts.
Music has been an integral part of human culture throughout history, captivating individuals across various ages and societies. It has played a significant role in human civilization for centuries, serving multiple purposes including entertainment, communication, and emotional expression.
In recent times, advancements in neuroscientific research have begun to shed light on the intricate relationship between music and the brain. Researchers have conducted numerous studies to examine how music influences emotions, memory, attention, and overall cognitive functioning. These investigations have revealed intriguing insights into the profound effects that music can have on the human brain.
This report aims to investigate the impact of music on different brain functions, including cognitive, emotional, and physiological aspects. By drawing upon a comprehensive review of existing literature, encompassing studies from disciplines such as neuroscience, psychology, and music therapy, aiming to provide a valuable resource for researchers, clinicians, educators, and individuals interested in understanding and harnessing the potential benefits of music for brain health and overall well-being for the benefit of all those around us.
Understanding the transformative power of music and its potential applications in both educational and therapeutic settings can pave the way for innovative interventions that enhance cognitive functioning, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
By delving into the intricate relationship between music and the brain, we can unlock the full potential of this universal art form and harness its benefits for individuals across diverse populations.
BACKGROUND
The impact of music on emotions is well-documented. Certain melodies, harmonies, and rhythms have the ability to evoke powerful emotional responses, ranging from joy and happiness to sadness and nostalgia. Understanding how music influences emotions is crucial for harnessing its potential in therapeutic interventions, as it can be used to regulate mood, reduce stress, and promote emotional well-being.
Research conducted by Harvard Medical School has shown that music has a significant impact on memory. Listening to music can enhance memory performance by improving encoding, consolidation, and retrieval processes. The mnemonic properties of music, such as its rhythmic structure and melodic patterns, can serve as effective cues for memory recall. This finding has important implications for educational settings, where incorporating music into learning activities can optimize memory retention and enhance academic performance.
The effects of music on attention and cognitive functioning have garnered considerable interest. Studies have demonstrated that certain types of music can enhance attentional focus, cognitive flexibility, and information processing speed. The synchronization between music and cognitive processes can create a state of heightened cognitive arousal, leading to improved cognitive performance in various tasks.
The Cognitive Effects of Music
1.1.
Memory Enhancement:
Many studies have shown that music can improve memory performance.
There is a research study called the “Mozart effect” suggesting that when a person listens to classical music, particularly some of Mozart’s compositions, it can enhance spatial-temporal reasoning skills which is being able to look at a shape and imagine what it would look like from another angle or if it were to be cut in half. This discovery can lead to learning and recalling lyrics or melodies that can engage the brain’s memory networks, helping aid people in remembering and recalling information.
The memory-enhancing effects of music can be attributed to the way that it is able to activate different regions of the brain that engage in memory processing. Parts of the brain such as the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex play important roles in encoding, consolidating, and retrieving information.
Music also acts as a helpful tool for our memory by providing organizational cues. The rhythmic structure and melodic patterns in music can serve as mental frameworks that can aid in memory formation. For example, when information is put into the form of a song or melody, it is often easier to remember the song and tune than just the words on a page.
The emotional impact of music also plays a significant role in memory enhancement. For instance, when music causes strong emotions, it can create a more vivid and memorable experience, which can lead to improved encoding and retrieval of associated information. This emotional engagement can be particularly beneficial when studying or trying to remember specific events or experiences.
Music can also have a positive impact on motivation and mood which can indirectly influence memory performance. When individuals are in a positive and/or motivated state, they are more likely to engage in learning and memory tasks with enthusiasm and perseverance. This positive mindset and emotional state can facilitate information processing and consolidation, leading to enhanced memory performance. Music can serve as a mood regulator, helping individuals to regulate their emotional state during learning and recall and therefore improves their overall memory performance and even their emotional well-being.
The effects of music on memory has been found to have varying effect on many different people. This can be because of the differentiating personal preferences and the specific characteristics of the music being listened to.
Studies by the Cognitive Neuroscience Society have shown that individuals tend to have a stronger memory response to music they personally enjoy. The complexity and structure of the music, such as the presence of lyrics, tempo, and rhythm, can also influence its impact on memory.
The cognitive effects of music on memory are multifaceted. Music can enhance focus, attention, and engagement, which can lead to improved memory encoding. The structure and organization of music can serve as mnemonic devices, aiding in memory retrieval.
Music can influence motivation, mood, creativity, and context-dependent memory, all of which contribute to enhanced cognitive performance and memory. By leveraging the cognitive benefits of music, individuals can optimize their memory abilities and overall cognitive functioning.
Music can serve as a context cue, facilitating memory retrieval through context-dependent memory. When individuals study or learn information in the presence of specific music, the music itself can act as a retrieval cue, aiding the recall of the associated information. This phenomenon, known as state-dependent memory, suggests that returning to the same musical context during recall can enhance memory retrieval.
Music has a powerful impact on memory. It can improve memory performance by helping us encode and retrieve information more effectively. The rhythmic and melodic qualities of music provide a structure that aids in memory formation. Emotionally engaging music enhances our ability to remember.
Music also captures our attention and focus, leading to better memory encoding. It can boost motivation and mood, which positively influence memory. Additionally, music stimulates creativity and divergent thinking, expanding our cognitive abilities beyond memory.
Applying these findings to education, therapy, and everyday life can have numerous benefits. Using music in learning environments can enhance memory and cognitive performance. Music therapy can help to aid individuals with cognitive impairments by improving their memory and emotional well-being. Utilizing music as a memory aid or as a cue in specific contexts can help with memory recall.
It’s important to consider personal preferences when using music for memory enhancement. Different people respond differently to various types of music, so choosing music that resonates with individuals is key to optimizing memory performance.
By harnessing the cognitive effects of music on memory, we can improve our ability to learn, enhance cognitive functioning, and enhance the overall quality of life.
1.2.
Attention and Focus:
The influence of music on attention and focus has been a topic of great interest and investigation. Studies have consistently demonstrated that music can capture and sustain attention, making it an effective tool for enhancing focus.
One key aspect to consider is the type of music that is being listened to. Instrumental tracks, especially those without lyrics, have been found to be particularly beneficial for attentional tasks for memory enhancement purposes but also for attention and focus.
The absence of lyrics reduces potential distractions and cognitive load, allowing individuals to direct their attention more effectively. The effects of music on attention and focus are especially pronounced in environments with distractions.
In noisy or disruptive settings, background music can act as a masking agent, reducing the impact of external disturbances and helping individuals maintain their focus. The rhythmic and predictable nature of music can provide a structured auditory environment that guides attention and filters out all irrelevant stimuli.
The arousal and emotional engagement induced by music also contribute to its impact on attention and focus. Music has the ability to evoke various emotions, such as excitement, calmness, or nostalgia, depending on its characteristics and individual preferences. This emotional engagement can enhance motivation and increase alertness, facilitating sustained attention and concentration on tasks.
While some individuals may find certain types of music beneficial for their focus, others may find it distracting. Understanding one’s own preferences and experimenting with different musical genres and styles can help identify the optimal conditions for enhancing attention and focus. The relationship between music and attention is complex and can vary depending on individual factors, such as personal preferences and cognitive abilities.
The impact of music on attention and focus extends beyond immediate task performance. Research suggests that regular engagement with music, such as music training or active music participation, can lead to long-term improvements in attentional control and cognitive flexibility. Learning to play a musical instrument, for example, involves sustained attention, fine motor skills, and the ability to coordinate multiple tasks simultaneously, all of which contribute to the development of attentional skills.
Research conducted by the Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience has shown that the tempo and rhythm of music can influence attention and focus. Upbeat and fast-paced music tends to increase arousal levels and can enhance alertness and engagement. This can be particularly useful when individuals need to tackle tasks that require sustained attention and quick response times, such as during high-pressure situations or demanding physical activities. Slower-tempo music, such as classical or ambient music, can promote a sense of calmness and relaxation. This can be beneficial for individuals who need to reduce stress and anxiety levels in order to focus better. Slow-tempo music can create a soothing environment that facilitates a state of deep concentration, allowing individuals to immerse themselves fully in their tasks.
Interestingly, the influence of music on attention and focus can vary depending on the complexity of the task. For simple and repetitive tasks, music can enhance performance by providing a rhythmic structure that helps individuals maintain a steady pace and minimize monotony. However, for more complex and cognitively demanding tasks that require high levels of concentration and mental effort, music may become a distraction and hinder performance. In these cases, a quiet and distraction-free environment is often recommended to optimize focus and cognitive processing.
Individual preferences also play a significant role in the effects of music on attention. What works for one person may not work for another. Some individuals may find certain genres or specific songs highly engaging and conducive to their focus, while others may find them distracting. It’s important for individuals to experiment and identify the type of music that best suits their attentional needs and personal preferences.
It’s worth noting that the effects of music on attention and focus can be influenced by individual factors such as musical expertise and familiarity. Musicians and individuals with extensive music training may have developed enhanced auditory processing skills and attentional control, allowing them to effectively integrate music into their cognitive processes without sacrificing focus.
Music can have both positive and negative effects on attention and focus, depending on factors such as tempo, the complexity of the task, individual preferences, and musical expertise. Fast-paced music can increase arousal and engagement, while slower-tempo music can induce relaxation and calmness. The relationship between music and attention is complex, and finding the right balance between music and task demands is essential.
By understanding these dynamics, individuals can harness the power of music to optimize their attentional abilities and improve their focus and productivity in various contexts.
Music has the potential to enhance attention and focus, particularly when instrumental tracks without lyrics are used. The emotional engagement, arousal, and masking effects of music can help individuals maintain their attention and concentration, especially in distracting environments. Long-term engagement with music through activities like music training can also promote attentional control and cognitive flexibility.
By leveraging the power of music, we can optimize our cognitive performance and improve our ability to stay focused and engaged in various tasks and settings.
1.3.
Cognitive Processing Speed:
Music has a profound impact on the human brain, and its effects go beyond mere enjoyment and entertainment. One fascinating aspect of music’s influence is its ability to affect cognitive processing speed. Cognitive processing speed refers to the rate at which the brain processes information and performs mental tasks.
Listening to fast-paced and stimulating music has been shown to enhance cognitive processing speed. When individuals engage with music that has a higher tempo, it activates various regions of the brain responsible for attention, memory, and motor coordination. This stimulation leads to an increased firing of neural connections and an overall enhancement in cognitive functioning.
Research according to the National Institutes of Health has demonstrated that the brain synchronizes its neural activity to the beat and rhythm of music. This synchronization phenomenon, known as entrainment, enables the brain to process information more efficiently and effectively. The rhythmic patterns and tempo of fast-paced music provide a structured framework that guides the brain’s processing speed, leading to improved performance in tasks requiring mental agility.
One area where the effects of music on cognitive processing speed are particularly noticeable is during physical exercise. Studies have shown that listening to energizing music while working out can enhance performance and endurance. Fast-tempo music can increase motivation and arousal levels, leading to improved focus and reaction time. This heightened cognitive processing speed enables individuals to execute movements more rapidly and accurately, enhancing their overall athletic performance.
The benefits of fast-paced music extend beyond exercise. Engaging with stimulating music can also enhance cognitive processing speed during mentally demanding tasks. For instance, when performing complex problem-solving activities, listening to upbeat music can increase alertness and mental energy, allowing individuals to process information more swiftly. This heightened cognitive speed can lead to improved creativity, critical thinking, and decision-making abilities.
The effects of music on cognitive processing speed can vary between individuals. Personal preferences, cultural background, and previous musical experiences can influence the extent to which music affects cognitive functioning. Additionally, the specific genre or style of music can also play a role in determining the impact on cognitive processing speed. While fast-paced music tends to have an energizing effect, different genres may have distinct cognitive effects, and individual responses can differ.
Music has a remarkable influence on the human brain, including its impact on cognitive processing speed. Listening to fast-paced, stimulating music can increase cognitive processing speed, enhancing performance in various activities such as exercise and mentally demanding tasks.
The synchronization of neural activity to the beat and rhythm of music provides a structured framework for the brain to process information more efficiently.
By understanding the relationship between music and cognitive processing speed, we can explore how music can be utilized to optimize cognitive functioning and improve various aspects of human performance.
Emotional and Psychological Effects of Music
2.1.
Mood Regulation:
Listening to music activates various regions of the brain associated with emotion processing, memory, and reward. When we hear music, the brain releases neurotransmitters like dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. This release of dopamine can enhance mood and create a sense of pleasure and satisfaction. Music can also stimulate the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers and mood elevators.
The effects of music on mood regulation can be seen in various situations. For example, upbeat and energetic music can boost mood and increase feelings of happiness and motivation. This type of music often has a fast tempo and a positive rhythm, which can encourage movement and physical activity, leading to a release of endorphins and a sense of vitality.
Slow and calming music can induce relaxation and reduce stress levels. Soft melodies, gentle rhythms, and soothing sounds can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting a state of calmness and tranquillity. This type of music is often used in therapeutic settings to aid in stress reduction and promote sleep.
It can also evoke strong emotional responses, especially when it is associated with personal memories or experiences. Certain songs or melodies can transport us back to specific moments in our lives, evoking nostalgia, joy, or even sadness. This emotional connection to music can be a powerful tool for mood regulation, as it allows individuals to express and process their emotions in a nonverbal and deeply personal way.
Music has also been found to have a positive impact on mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Studies have shown that listening to music can reduce symptoms of depression, elevate mood, and increase self-esteem. It can provide a sense of comfort and connection, serving as a form of emotional support during challenging times.
Music therapy, a specialized form of therapy that uses music to address emotional, cognitive, and social needs, has been shown to be effective in improving mood regulation and overall well-being.
Trained music therapists work with individuals to create personalized music experiences that promote self-expression, emotional exploration, and relaxation.
Musical preferences are highly subjective, and what may be soothing and uplifting for one individual may not have the same effect on another. Personal associations, cultural backgrounds, and individual experiences all play a role in determining how music influences mood.
Music has a profound effect on mood regulation. It can evoke a wide range of emotions, stimulate the release of neurotransmitters associated with pleasure and reward, and provide a means for self-expression and emotional processing.
Whether it’s through upbeat and energizing music or calming and soothing melodies, music has the power to positively impact emotional well-being and contribute to a healthier mind.
2.2.
Stress Reduction:
Stress reduction is one of the prominent benefits of music, as it has been consistently shown to have a profound impact on promoting relaxation and alleviating stress. The choice of music can play a crucial role in achieving this desired effect. For instance, slow-tempo music, classical compositions, or nature sounds have been found to have a particularly calming influence on the body and mind.
Listening to relaxing music before or during stressful situations has been shown to effectively reduce stress hormone levels, such as cortisol, and mitigate feelings of anxiety. This can be especially beneficial in high-pressure environments, such as workplaces or academic settings, where stress levels can significantly impact performance and well-being.
The soothing qualities of music have been attributed to its ability to engage the autonomic nervous system, which controls various physiological processes in the body, including heart rate, blood pressure, and stress responses. When exposed to relaxing music, the body tends to undergo a series of beneficial changes. Heart rate and blood pressure may decrease, muscles may relax, and breathing may become slower and more regular. These physiological responses contribute to an overall sense of calmness and tranquillity.
Music has the ability to distract individuals from stressful thoughts or external stressors. By redirecting attention to the pleasant and engaging aspects of the music, individuals can temporarily shift their focus away from stressors, allowing them to experience a temporary respite from the pressures of everyday life. This distraction-based approach has been effective in managing acute stress and enhancing coping mechanisms.
The effectiveness of music in stress reduction may vary depending on personal preferences and individual differences. Different individuals may have varying responses to different types of music, and it is important to consider individual preferences and tastes when utilizing music as a stress reduction tool. Some individuals may find classical music or instrumental compositions more relaxing, while others may prefer nature sounds or ambient music. Exploring and discovering one’s own preferences can maximize the stress-reducing benefits of music.
In addition to listening to relaxing music, active engagement with music can also play a role in stress reduction. Playing a musical instrument, singing, or participating in group music-making activities can provide a creative outlet and serve as a form of self-expression, which can be cathartic and alleviate stress. Music therapy, a field dedicated to utilizing music for therapeutic purposes, often incorporates active engagement with music to promote emotional well-being and stress reduction.
The stress-reducing effects of music are well-documented and supported by scientific research. By incorporating music into daily routines, particularly by listening to relaxing music or actively engaging with music, individuals can harness its powerful stress-reducing properties and enhance their overall well-being. As an accessible and enjoyable tool, music offers a valuable resource for individuals seeking to manage and mitigate the negative impacts of stress in their lives.
2.3.
Therapeutic Applications:
Therapeutic applications of music extend beyond mood regulation and stress reduction, encompassing a wide range of conditions and populations.
Music therapy, as an established field, utilizes music as a therapeutic intervention to address the physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs of individuals.
The effects of music therapy have been observed in diverse settings, including hospitals, rehabilitation centres, schools, and community programs.
One area where music therapy has shown significant benefits is in the treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Individuals with ASD often experience challenges in social communication and interaction. Music therapy provides a structured and engaging medium through which individuals with ASD can develop and improve their social and communication skills. Music interventions, such as improvisation, singing, and rhythmic activities, can facilitate emotional expression, promote social interaction, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with ASD.
In the context of dementia, music therapy has demonstrated remarkable effects in enhancing cognitive function, reducing behavioural symptoms, and improving the overall well-being of individuals. Music has a unique ability to evoke memories and emotions, even in individuals with advanced stages of dementia.
By using personalized playlists or engaging in group music-making activities, music therapy can tap into preserved musical memories, stimulate cognitive processes, and enhance mood and social engagement.
Chronic pain is another area where music therapy has been proven to be beneficial. Music interventions have shown promise in reducing pain perception, decreasing anxiety related to pain, and improving overall mood and emotional well-being in individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions.
The rhythmic and melodic aspects of music can serve as distractions from pain, while the emotional qualities of music can promote relaxation and emotional release.
Music therapy has been integrated into various mental health settings, offering support for individuals with depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Music interventions, such as listening to preferred music or engaging in songwriting and lyric analysis, can provide a means for emotional expression, facilitate insight and self-reflection, and promote emotional regulation.
Music therapy sessions in mental health settings often create a safe and supportive environment for individuals to explore their emotions, increase self-awareness, and develop coping strategies.
In addition to individualized therapeutic approaches, group music therapy sessions offer opportunities for social connection, community building, and shared experiences. Group music-making activities promote cooperation, communication, and empathy among participants. These sessions can be particularly valuable in promoting social inclusion and reducing feelings of isolation for individuals with disabilities, mental health conditions, or those experiencing social challenges.
Music therapy is a highly individualized and client-centred approach. Music therapists are trained professionals who assess each individual’s unique needs and tailor interventions accordingly. They utilize various music techniques, such as active music-making, receptive listening, improvisation, and music-assisted relaxation, to address specific goals and objectives.
Music therapy is a well-established and effective therapeutic modality that harnesses the power of music to address a wide range of physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs. Its applications span across conditions such as autism, dementia, chronic pain, mental health disorders, and more.
By utilizing music as a therapeutic tool, music therapy promotes self-expression, facilitates social interaction, enhances cognitive function, and improves overall well-being.
Continued research and integration of music therapy into various healthcare and educational settings hold promise for expanding its therapeutic reach and improving outcomes for individuals across diverse populations.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this comprehensive research report provides a thorough exploration of the effects of music on the brain, encompassing psychological, physiological, and cognitive dimensions. By examining the influence of music on memory, emotions, attention, and overall cognitive functioning, we gain valuable insights into the multifaceted ways in which music impacts our brain and behaviour.
Regarding cognitive effects, music has been found to have a significant impact on memory enhancement. Numerous studies have demonstrated that listening to music can improve memory recall, particularly when the music is associated with specific events or experiences. Furthermore, music has shown promising potential in aiding memory retention and retrieval in individuals with cognitive impairments, such as those with Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia.
Music also plays a crucial role in attention and focus. Research suggests that certain types of music, such as instrumental music or music with a moderate tempo, can enhance attention and cognitive performance. In contrast, loud or distracting music may hinder concentration and cognitive tasks.
By understanding the relationship between music and attention, we can leverage music as a tool to optimize focus and productivity in various domains, including education, work, and creative pursuits.
Music has been found to influence cognitive processing speed. Fast-paced and stimulating music can accelerate cognitive processes, leading to quicker information processing and response times. This finding has implications for activities that require rapid cognitive processing, such as sports, video games, and problem-solving tasks.
Research done by various places has consistently demonstrated music’s ability to regulate mood. Music has the power to elicit a wide range of emotions, including happiness, sadness, nostalgia, and excitement. Listening to music that aligns with an individual’s emotional state or desired mood can help regulate and enhance emotional experiences. This phenomenon has been utilized in various therapeutic settings, including music therapy, where music is used to facilitate emotional expression, stress reduction, and overall well-being.
Music has been shown to reduce stress levels. Engaging with music, whether through active listening, playing an instrument, or participating in group music-making activities, has been associated with a decrease in stress hormones and subjective reports of stress. Music’s ability to elicit relaxation responses and promote a sense of calmness makes it a powerful tool in stress management and coping strategies.
Beyond mood regulation and stress reduction, music has therapeutic applications in various domains, including mental health, pain management, and rehabilitation. Music therapy has been shown to improve symptoms of depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Additionally, music has been used successfully to alleviate pain perception, enhance motor function and coordination, and support recovery in individuals with neurological conditions or physical injuries.
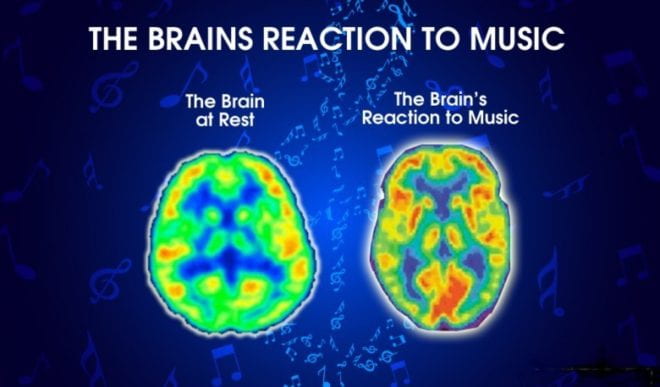
On a physiological level, music has been found to activate multiple regions of the brain. Neuroimaging studies have revealed that listening to music engages areas involved in auditory processing, emotion regulation, and memory. The brain’s response to music involves intricate neural networks and complex interplay between different brain regions.
Furthermore, music has been linked to the activation of the dopaminergic reward system in the brain. The release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, is triggered by pleasurable experiences, including listening to music. This suggests that music can evoke feelings of pleasure and contribute to a sense of reward, which may explain its strong emotional impact and the motivation to engage with it.
Lastly, music has demonstrated its influence on motor coordination. Studies have shown that rhythmic music can enhance motor skills and improve coordination and synchronization. This has implications for various domains, such as physical exercise, dance, and rehabilitation therapies where rhythmic cues can be utilized to facilitate motor learning and movement coordination.
The research findings presented in this report underscore the profound effects of music on the brain. Music has the potential to enhance memory, improve attention and cognitive processing speed, regulate mood, reduce stress, and offer therapeutic benefits. It activates diverse brain regions, stimulates the reward system, and supports motor coordination.
Understanding the intricate relationship between music and the brain can inform the development of innovative interventions, treatments, and personalized approaches in fields such as education, healthcare, and mental well-being.
Continued research in this field will further expand our knowledge of the underlying mechanisms and applications of music, contributing to our understanding of its powerful impact on human cognition, emotions, and behaviour.
RESEARCH REPORT BIBLIOGRAPHY
Baker, Mitzi. “Music Moves Brain to Pay Attention, Stanford Study Finds.” News Center, Stanford Medicine, 1 Aug. 2007, https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2007/07/music-moves-brain-to-pay-attention-stanford-study-finds.html
“Home.” Cognitive Neuroscience Society, www.cogneurosociety.org/.
“Brain Basics: Know Your Brain | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.” Www.ninds.nih.gov, www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/public-education/brain-basics/brain-basics-know-your-brain#:~:text=The%20brain%20is%20the%20most.
Budson, Andrew E. “Why Is Music Good for the Brain?” Harvard Health Blog, Harvard Health Publishing, 7 Oct. 2020, www.health.harvard.edu/blog/why-is-music-good-for-the-brain-2020100721062.
Gayle, Katie. “What Are the Effects of Music on the Brain?” Www.creativesoulmusic.com, www.creativesoulmusic.com/blog/what-are-the-effects-of-music-on-the-brain.
“How We Process Music | Neuroscience for Musicians.” Www.youtube.com, www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y7tiIv_3yho.
Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works.” Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2023, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/anatomy-of-the-brain .
“Keep Your Brain Young with Music.” Www.hopkinsmedicine.org, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/keep-your-brain-young-with-music#:~:text=If%20you%20want%20to%20keep.
McCollum, Sean. “Your Brain on Music: The Sound System Between Your Ears.” Kennedy-Center.org, 2020, www.kennedy-center.org/education/resources-for-educators/classroom-resources/media-and-interactives/media/music/your-brain-on-music/your-brain-on-music/your-brain-on-music-the-sound-system-between-your-ears/.
“Music Therapy.” Raising Children Network, https://raisingchildren.net.au/autism/therapies-guide/music-therapy#:~:text=Does%20music%20therapy%20help%20autistic.
Shepherd, Becks. “How Does Music Affect Your Brain?” Livescience.com, 15 Dec. 2022, www.livescience.com/how-does-music-affect-your-brain.
The University of Central Florida. “Your Brain on Music.” Pegasus Magazine, University of Central Florida, 2017, www.ucf.edu/pegasus/your-brain-on-music/.
University of Nevada, Reno. “Releasing Stress through the Power of Music | Counseling Services.” The University of Nevada, Reno, www.unr.edu/counseling/virtual-relaxation-room/releasing-stress-through-the-power-of-music#:~:text=Faster%20music%20can%20make%20you.