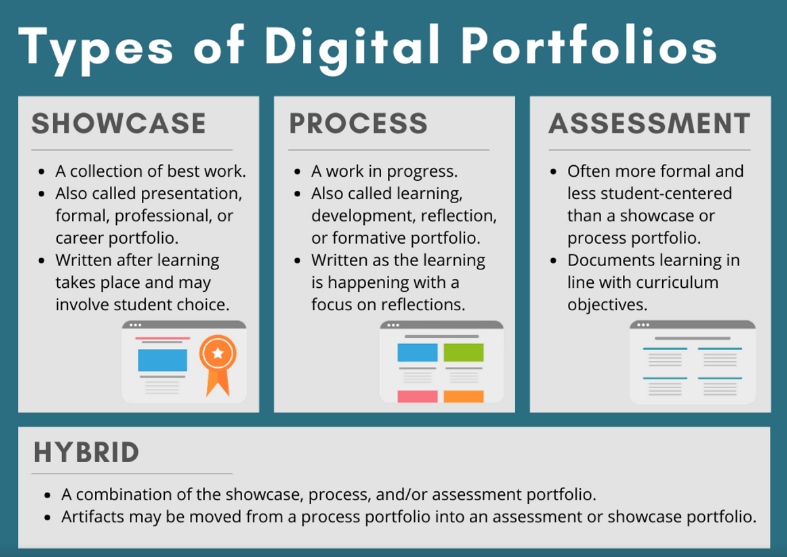
What type of ePortfolios will students create? Let’s break down the 4 most popular types and how they’re used.
There are four main types or functions of ePortfolios in schools and higher education:
- Showcase or presentation
- Process or learning
- Assessment
- Hybrid
Let’s take a look at these four types of portfolios
1) Showcase or Presentation Portfolio: A Collection of Best Work
These types of portfolios focus on the portfolio as a product and are also typically called professional portfolios, formal portfolios, or career portfolio.
The content that’s added to showcase portfolios is written after the learning takes place, often with reflection from the student. Some schools adopt the mantra of, “collect, select, reflect, connect” (PDF Hughes, 2008). The connect element is an interesting – it involves sharing student work with others (probably beyond the teacher) and actively seeking an audience and feedback.
The showcase portfolio is often used to share a student’s best achievements or evidence of learning. Students are generally given the choice to decide what is published.
These sorts of portfolios can assist with self-marketing, online branding, or building a positive digital footprint. In higher education, we see commonly see showcase portfolios that highlight a student’s CV or resume to suit a particular purpose such as attracting potential employers.
2) Process or Learning Portfolio: A Work in Progress
The second type of portfolio that we commonly see is more of a running record of learning. The purpose is to capture the learning process. It’s also called a development portfolio, a reflection portfolio, or a formative portfolio.
Entries and artifacts are added during the learning process. A process portfolio is not always a collection of a student’s best work; it can include a variety of learning attempts or unpolished documentation along with reflections on struggles and challenges.
These types of portfolios demonstrate a work in progress and allow for self-assessment and reflection.
One trap you might want to try to actively avoid if you’re using process portfolios is the “digital dump”. That is, over time, students can end up adding a lot of artifacts to their portfolio without much organisation, reflection, or purpose. A process portfolio is a fabulous way to demonstrate learning as it happens but students may want to consider how to keep the portfolio well-organised and meaningful.
3) Assessment Portfolio: Used For Accountability
The assessment portfolio is used to document what a student has learned, or demonstrate that they have mastered elements of the curriculum.
Here, reflective comments will focus on how artifacts align with curriculum objectives.
These types of portfolios may be more formal than a showcase or process portfolio. While they may be very useful within the school environment to provide evidence of learning to teachers and administrators, an assessment portfolio may be less useful for overall student development.
Assessment portfolios are commonly part of certification programs or even part of requirements for earning a degree.
4) A Hybrid Approach
The 4th type of portfolio you’ll commonly come across is a combination of the showcase, process, and/or assessment portfolio.
Canadian EdTech leader George Couros explains how two types of portfolios can come together with some examples,
Learning [process] portfolio: If a student were to take a video of them reading in four consecutive months, you would see all readings over time to see development and growth.
Showcase portfolio: If a student were to take a video of them reading in four consecutive months, they would pick the best one from the four samples.
What is beautiful in using a portfolio is that you do not have to choose; you can do both.
Does this show the student’s progression over time (learning), or just the best stuff (showcase)? There are considerable benefits to both over time and a combination, from my experience, is the best path to pursue.
Some educators find it’s easiest to start out with a showcase portfolio, or a collection of best work. From there, they can evolve into the process or hybrid approach. You might also find your portfolios are fluid in nature, for example, students may move pieces from a process portfolio into either an assessment or showcase portfolio.
This movement might be through having multiple blogs, or through using blog posts for process entries and blog pages for documenting assessment or showcasing artifacts. Alternatively, tags and categories can be used to identify assessment pieces or “final work” within a student’s portfolio.
Making choices about which process artifacts to move to a more “final” product involves a great deal of deep consideration and reflection: a rich experience in itself for students.
Knowing which type(s) of portfolio you will be focusing on will help inform decisions around choosing a platform and building a template portfolio.